THE MAIN FUNCTIONS OF A CLUTCH
 |  |  |
BASIC |
COMFORT |
PROTECTION |
 |  |  |
- Transmit all the torque.
Couple and uncouple the engine and the gearbox. - Enable the driver to control the torque to be transmitted.
Change gear smoothly.
Reduce the vibrations between the engine and the gearbox. - All clutches are designed to slip in the event of excessive torque in order to protect the engine and the transmission.
The clutch and the engine flywheel must be capable of dissipating heat. Premature failures usually result in clutch slippage.
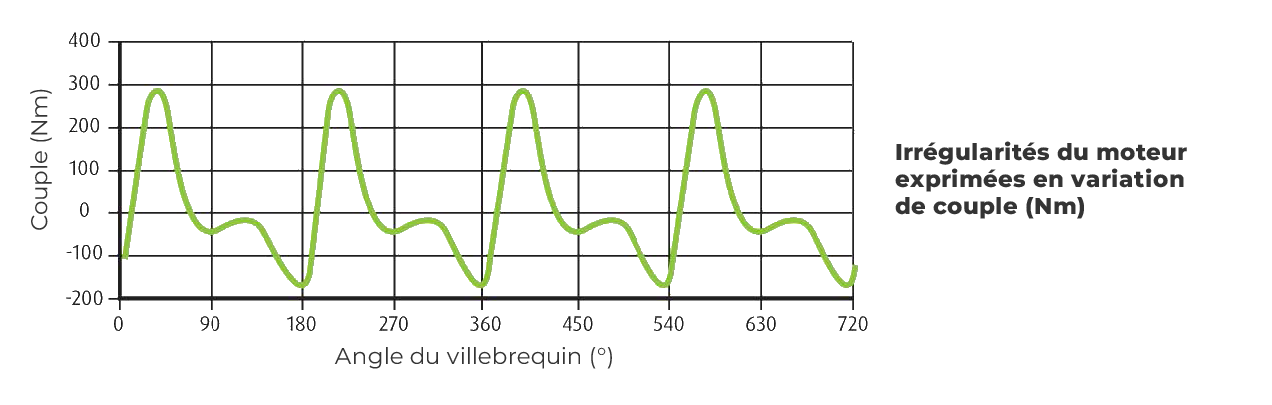
ENGINE ACYCLISM: DEFINITION
Internal combustion engines can be characterized by the alternating compression and combustion phases.
The cyclic pressure variations inside the cylinder result in variations in the speed of rotation. These variations are called acyclism.
Acyclism causes an uneven speed of rotation of the crankshaft. This is also called torsional vibration.
 |
GOOD TO KNOW
 | Perceived noise can be caused by poor filtration of vibrations and acyclism. It is the result of the rotation of the crankshaft + engine flywheel + clutch assembly, which is subject to cyclical irregularities. |





